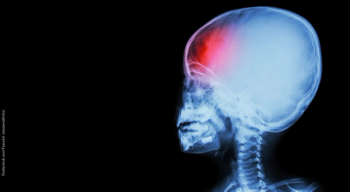
Physicians must understand current diagnostic criteria for pediatric migraine and its variants, and exercise their best clinical judgment regarding treatment.

Physicians must understand current diagnostic criteria for pediatric migraine and its variants, and exercise their best clinical judgment regarding treatment.

The American Academy of Pediatrics’ (AAP) has updated its Allergy and Anaphylaxis Emergency Action Plan for the treatment of infants at risk for an allergic emergency.

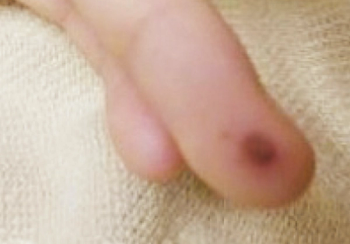
A 15-year-old Caucasian male with a past medical history of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder presents to the hospital emergency department with a 1-week history of fever, headache, arthralgias, vomiting, and rash.
Oral health should be central to your patients' daily routines, but it's too often buried in a long list of priorities.

Healthcare providers must communicate to their adolescent and young adult patients the dangers of electronic nicotine delivery systems.

Many parents and professionals have these misconceptions about allergies and other unusual findings.
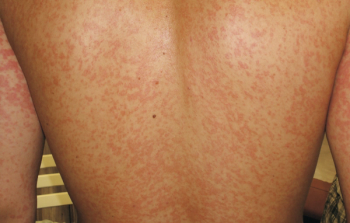
A 16-year-old boy develops a diffuse, rapidly progressive eruption on his trunk, face, and extremities 4 days after starting oral amoxicillin for presumed strep throat. He presents to the emergency department (ED) where Stevens-Johnson syndrome is considered. The ED physician notes no mucous membrane involvement.

A retrospective study of data from a regional community pharmacy chain in the Midwest encompassing 98 zip codes found that almost 1 in 8 new prescriptions for individuals aged up to 18 years went unfilled after the pharmacy received the prescription.

Exposure to acid-suppressive medications or antibiotics in the first 6 months of life is associated with development of allergic disease, according to a retrospective study in more than 750,000 children from within 35 days of birth until aged at least 1 year.
Investigators compared the accuracy of an American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) practice guideline algorithm for diagnosing of urinary tract infection (UTI) in 2- to 23-month-olds with a new tool (UTICalc; University of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania) that first estimates UTI probability based on clinical variables and then, if laboratory testing is performed, updates the estimate based on the results.