
A look back at the FDA submissions and regulatory decisions in the pediatric health care space from January 2026.

A look back at the FDA submissions and regulatory decisions in the pediatric health care space from January 2026.

Deep transfer learning models may enable more accurate, globally applicable prediction of spoken language outcomes in deaf children receiving cochlear implants.

A study found that dried blood spot screening can identify presymptomatic type 1 diabetes in children, reducing the risk of diabetic ketoacidosis.

A study found that an FDA-cleared device was safe for pediatric patients with ADHD but did not significantly improve symptoms vs sham treatment.

Family systems assessments help clinicians understand how parenting, co-parenting, and family relationships shape children’s mental health.

AbbVie submitted FDA and EMA applications for upadacitinib (RINVOQ) in adults and adolescents with non-segmental vitiligo, supported by phase 3 Viti-Up data.

About one-fourth of young children who experience a concussion continue to show symptoms months after injury.
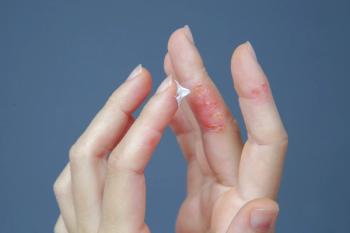
Phase 2 INTEGUMENT-INFANT study results show roflumilast cream 0.05% was well tolerated and improved disease severity in infants with atopic dermatitis.
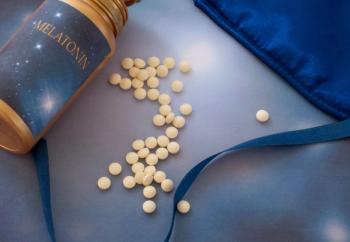
Experts are urging caution with pediatric melatonin use, citing rising consumption, inconsistent dosing, and limited long-term safety data.

The FDA has issued a CRL for Anaphylm sublingual epinephrine, citing human factors and PK study needs; resubmission is anticipated in Q3 2026.

A comprehensive review of high-quality studies found no evidence that prenatal paracetamol use increases the risk of autism, ADHD, or intellectual disability.

Get caught up with Contemporary Pediatrics! This list helps you navigate our top stories from the week, all in one place.

Increasing numbers, complexity, and severity of maternal chronic conditions are associated with a dose-response rise in severe neonatal morbidity and mortality.

Youth suicide data highlight firearm safety counseling and universal screening as key prevention tools, especially for youth without prior mental health contact.

A study found that children with both a low 5-minute Apgar score and low umbilical cord blood pH at birth had an increased risk of ADHD.

In a recent study, targeted sodium supplementation guided by urine sodium levels was associated with improved early weight gain in very preterm infants.

AAP policy outlines when pediatricians may provide care to parents during child visits, emphasizing benefits, legal considerations, and documentation safeguards.

AAP updates guidance on children’s digital media use, urging child-centered design and system-level action beyond screen time limits.

Prescribing increased after adolescent approval but remains uncommon.

A study found a dose-response increase in severe neonatal morbidity or mortality among infants born to mothers with multiple preexisting chronic conditions.

Cardiovascular risk factors beginning in infancy may influence cognitive function by young adulthood, highlighting the importance of early heart health promotion.

Three-year EMBARK data show ELEVIDYS slows functional decline in ambulatory Duchenne patients, extending earlier 2-year efficacy findings.

More than half of infants with myelomeningocele experience sleep-disordered breathing before hospital discharge, with prematurity driving risk.

A study found that a deep learning model using baseline fundus images can accurately predict myopia progression and high myopia risk.

A study found that individuals with ADHD traits in childhood had increased odds of physical multimorbidity and disability by midlife.

Eye-tracking technology revolutionizes autism diagnosis, enabling earlier detection and intervention for children, enhancing clinical efficiency and accuracy.

A study found that nonmedical childhood vaccine exemptions have increased significantly across US counties since 2010.

FDA accepted centanafadine NDA for priority review, supported by phase 3 trials showing efficacy in children, adolescents, and adults with ADHD.

A study found significant gaps in sudden unexpected death in epilepsy awareness and risk management.

AAP updated guidance supports therapeutic hypothermia for term infants with moderate to severe HIE, emphasizing early initiation and specialized care.