
It sometimes can be difficult for maturing pediatricians to maintain the level of confidence in their talents that they had when they left residency.

It sometimes can be difficult for maturing pediatricians to maintain the level of confidence in their talents that they had when they left residency.

Survivors of childhood cancers who received therapeutic radiation to the head or neck have an increased risk of stroke later in life that requires vigilant surveillance and monitoring.

Infants in the United States still may not be getting enough vitamin D in their diet or daily environment, according to new findings.

Pfizer's pneumococcal 13-variant conjugate vaccine (Prevnar 13) was approved by the FDA for active immunization of children aged 6 weeks through 5 years for the prevention of invasive disease caused by 13 Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes.

Children with psoriasis may be more prone to experiencing psychiatric disorders such as anxiety or depression, compared with young people who do not have the skin issue, new research indicates.

A new report suggests that SIDS is associated with a defect in 1 or more components of the medullary 5-hydroxytryptamine system.

The longer children sleep at night, the less likely they will experience faulty regulation of heart rhythm while sleeping.

A common question in our profession is: "Why did this child develop this disease at this time?"

In an analysis of three common antiseizure medications used to treat absence epilepsy in children, ethosuxomide was associated with the best outcomes overall, compared with lamotrigine and valproic acid.

During the 2005-2006 school year, the New York City Department of Education removed whole milk from cafeterias in all the city's public schools.

Healthcare teams at several Massachusetts community health centers are trying out a "third way" for treating obesity in the primary care setting.

A 14-year-old girl comes to your office complaining of having a headache every day for the last 3 months.

A brief bout of hearing loss during childhood can result in chronic hearing deficits in later years, according to research.

A 51⁄2 -year-old girl was brought to her pediatrician’s office by her mother, who reported that her daughter had a 1-week history of nasal congestion, intermittent fever, and cough that was worse in the morning and at night. The child was alert and smiling and appeared to be in no apparent distress.
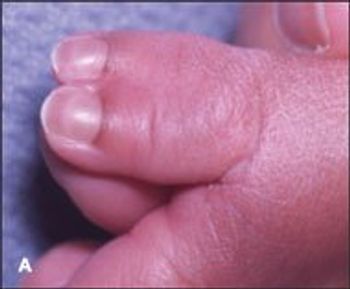
Complete duplication of the left thumb in a baby boy was noted at birth; a radiograph of the thumb showed 2 proximal and distal phalanges with 1 first metacarpal bone. He also had fusion and incomplete bony duplication of the right thumb; a radiograph of this digit showed normal proximal and distal phalanges plus a small tiny bony remnant of the proximal and distal phalanges of an accessory thumb.
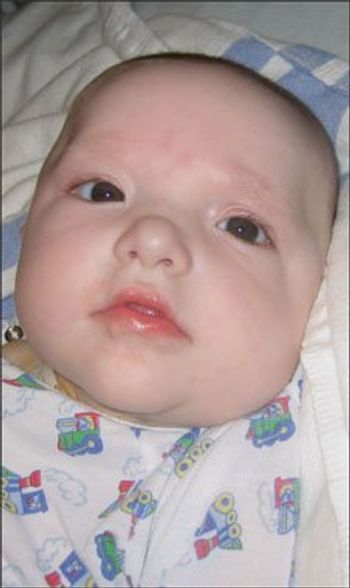
A 6-month-old boy with dysmorphic facial features, ear anomalies, and hypospadias brought for evaluation of elevated temperature and generalized seizure. Infant born at term to a 37-year-old mother via uncomplicated cesarean delivery.

ABC's of an office emergency Puzzler : Fever, rash, and polyarthralgia Dermcase : Hereditary, pigmented spots Ovarian masses in adolescents

Childhood obesity, glucose intolerance, and hypertension, but not hypercholesterolemia, predict premature death from endogenous causes.

Imagine that you are working in an outpatient pediatric practice one morning when a mother arrives with her 3-month-old infant who is in respiratory florid distress.

Chronic illnesses, including asthma and obesity, affect more than 25% of US children, but many children are able to overcome their conditions as time passes, according to new findings.

Finnish researchers analyzed data from a nutrition study that examined the effects of maternal diet during pregnancy and lactation on the development of type 1 diabetes.

Limited eye contact and communication abilities, cited as autism symptoms, often are not detectable in an infant's first few months but become more apparent as children reach 1 year of age.

Identifying pandemic H1N1 flu in children may not be as easy as administering rapid influenza tests, according to 2 studies.

Most of the articles were chosen for their basic interest to the general pediatrician.

Infants who had prenatal complications or who faced injuries at birth may benefit from hopping on the treadmill.

Infants diagnosed with flat head syndrome have increased chances of delayed physical and mental development, according to a new study.

Immediate auscultation continued into the 19th century until French physician Rene Theophile-Hyacinthe Laennec invented the first stethoscope.

The patient's mother says her child's brown spots have been present since the child was born.

The high-fat ketogenic diet, used to manage seizures in children with epilepsy, may have no enduring adverse events, according to new research.

Ask any pediatrician to name the viral infection responsible for the most identifiable syndrome with the most predictable seasonality, and their most likely response will be respiratory syncytial virus.