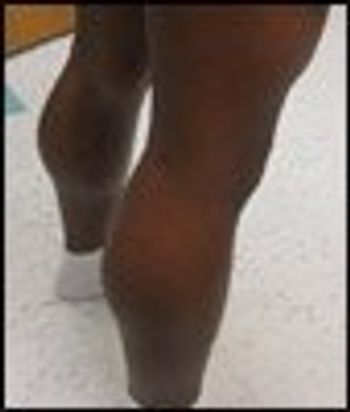
Otherwise healthy 9-year-old African American boy seen for first time for complaints of frequent exhaustion, particularly when climbing stairs or walking for long periods. He could no longer participate in sports because of inability to keep up with his peers. He had been toe walking and had become clumsier over the past year, tripping and falling more frequently. Besides a mild delay in walking (around 16 months), his mother had reported no outstanding gross motor delays in infancy. He was in a regular class in school, although he did receive extra help in math and reading.