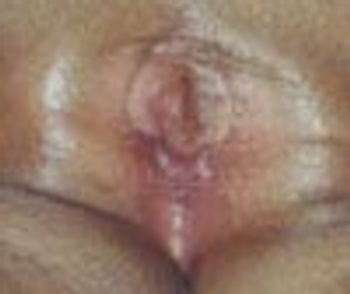
The mother of this 11-month-old girl was concerned that her infant’s vagina was almost obscured by a membrane. This was noted incidentally a few days earlier.

The mother of this 11-month-old girl was concerned that her infant’s vagina was almost obscured by a membrane. This was noted incidentally a few days earlier.
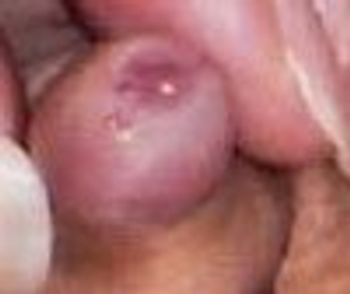
A 4-year-old boy was brought for evaluation of a tiny cystic mass on the penis. The lesion was first noted a year earlier when the foreskin became retractable.
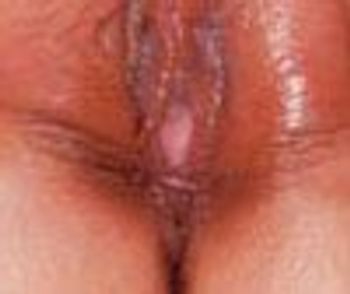
The mass protruding from the introitus of this 1-month-old girl was first noted at birth. She was born to a 26-year-old primigravida at term after an uncomplicated pregnancy and normal spontaneous delivery.
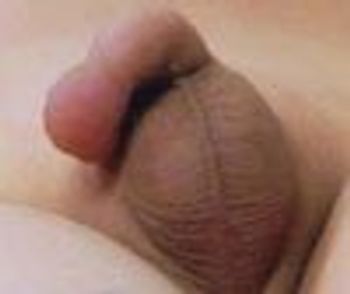
A 6-year-old boy presented with a swollen penis and lip within an hour after ingesting some peanuts.
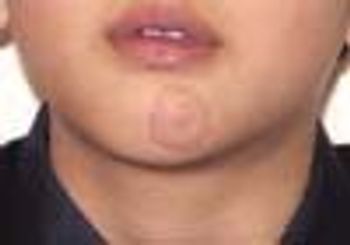
A 7-year-old boy was brought for evaluation of a rash on the chin that had appeared 2 weeks earlier. It was slightly itchy. The mother had applied a topical corticosteroid for a few days but then stopped because of worsening of the lesion.
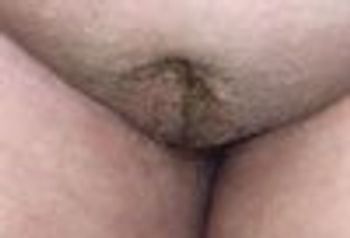
Premature Adrenarche: A 7-year-old girl had growth of pubic hair for the past 6months. The hair was initially limited to the labia majoraand then extended gradually into the pubic area. Isolated Scrotal Hair of Infancy: Infant was born at term to a 32-year-old gravida 2 para 3 after a normal vaginal delivery. Scrotal hair developedat age 1 month.

A discussion of three types of Genital Lesions: Sebaceous Gland Hyperplasia of the Penis, Varicocele, and Penile Dog Bite.

A discussion of three types of Genital Lesions: Concealed Penis, Balanoposthitis, and Scrotal Abscess.
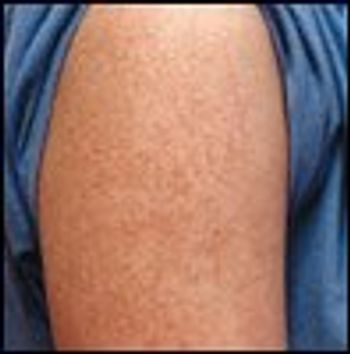
17-Year-old girl with a 7-month history of small, red papules on her arms and thighs. Rash is not painful or itchy. Otherwise in good health.

Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is the most common type of diabetes encountered in children. The incidence of T1DM in children is increasing in some populations. Early recognition of symptoms of T1DM is critical to avoid life-threatening metabolic decompensation. Such symptoms can include polyuria, polydipsia, fatigue, weight loss, urinary tract infection, vaginal candidiasis, and “fruity” breath. In the presence of clinical symptoms of hyperglycemia, diagnosis requires just 1 laboratory blood glucose measurement above the established threshold for the child’s age. In the absence of typical symptoms, a second abnormal blood glucose measurement on a different day is needed.

Although at present there is no cure for type 1 diabetes mellitus, good treatments are available that can enable affected children to lead healthy, active lives. Insulin regimens should be designed to optimize metabolic control while minimizing the risk of adverse events, such as hypoglycemic episodes, which can be more serious in children. Regimens of 3 in- jections per day work well for children who cannot receive an injection at lunchtime, while multiple daily injection (MDI) regimens provide more flexibility. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) can provide better quality of life than MDI regimens, but CSII requires a high level of motivation and carries its own risks. In all children, insulin regimens must be adjusted to accommodate the physiological changes of growth and development. Long-term follow-up is important to monitor for complications of diabetes.
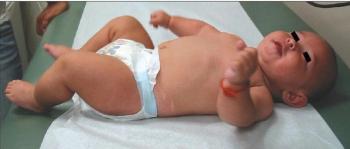
Four-month-old Hispanic boy brought for evaluation because of hypopigmented patches on his skin and a history of seizures. Infant was the product of an uncomplicated pregnancy; born at 40 weeks' gestation to a 16-year-old gravida 1, para 1 mother who received appropriate prenatal care. At birth, he had multiple hypopigmented patches on his face, torso, and extremities. At age 2 months, he was hospitalized for new-onset seizures.

The parents of this 5-month-old boy were concerned that his eyes were turned in toward the nose. The infant was otherwise healthy. Physical examination findings were normal. In particular, when a light source was projected onto the eyes, the light reflex was centered in both eyes.
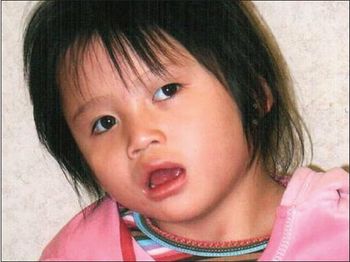
This 4-year-old girl was born to a 27-year-old gravida, 1 para 0 mother at 37 weeks' gestation via vaginal delivery. The pregnancy was uncomplicated. Apgar scores were 8 at 1 minute and 9 at 5 minutes. The child's birth weight, head circumference, and length were 3045 g, 33 cm, and 50 cm, respectively. Her mother noted global developmental delays (particularly in the areas of speech and fine motor skills), abnormal sleep habits, obstructive sleep apnea, and seizure disorder. Family history was unremarkable.

A discussion of two types of Genital Lesions: Smegma and Torsion of the Testis.

Sixteen-year-old African American girl with pruritic, painful lesions on both thighs that progressively worsened over 2 weeks and later spread to the trunk and upper and lower extremities.

African American girl born at 36 weeks' gestation to 24-year-old primigravida via spontaneous vaginal delivery at a community hospital. Apgar scores, 7 at 1 minute and 9 at 5 minutes. Grossly normal placenta, with a 3-vessel cord. On the second day of life, infant required several minutes of blow-by oxygen for a desaturation event and subsequent transfer to a level III neonatal ICU for further monitoring.

Ten-month-old girl with swelling of the left knee of 7 weeks' duration. Unable to bear weight on the left leg for the past 2 weeks. No fever or history of trauma to the area. Infant has good appetite for breast milk and formula, but possible malaise.

In children, most causes ofitching are the result of skin disease,not underlying systemic illness. The mostcommon dermatological causes of pruritusare atopic and contact dermatitis,urticaria, miliaria rubra, infections, insectbites or infestations, xerosis, and aquagenicpruritus. A careful history andphysical examination usually reveal thediagnosis. The location, chronicity, timeof occurrence, and nature of the itchingoffer important diagnostic clues, as doprecipitating factors, associated symptoms,drug use, exposure to infectious diseasesor pets, psychosocial history, past health,and family history. Treatment of the underlyingcause of itching should beaddressed whenever possible. Symptomatictreatment is essential to breakthe itch-scratch cycle.

Ultrasonography showed a large multiseptated cystic mass in the posterior part of the left side of the neck. No obvious vascular flow evident within the mass (Figures 3 and 4).

A discussion of three types of Genital Lesions: Phimosis, Paraphimosis, and Hypospadias.

17-Year-old female with a salmon-pink oval patch on her back. Three days after the patch appeared, a generalized eruption developed on her back. Eruption slightly pruritic. No antecedent upper respiratory tract infection. No prodromal symptoms.

During spring vacation, a previously healthy 4-year-old girl visited western Nebraska, where she and her family spent time along a river bank in a wooded area. After 4 days, her mother noticed 3 engorged ticks embedded in the child's scalp. The ticks were immediately removed and burned. The child also had a marble-sized swelling on the right side of her neck. Over the next few days, the child had temperatures that spiked to 39.4C (103F), with chills, generalized malaise, and weakness. There was no history of cough, myalgias, or headache.

Three-year-old boy limping on right foot after an unwitnessed fall from trampoline the day before. Pain controlled with ibuprofen. No history of chronic diseases or routine medication use.
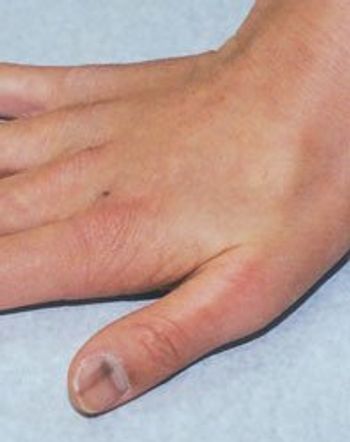
A brown band runs along the longitudinal axis of this teenager’s thumb.

The mother of this 5-week-old girl reports that her baby's head tilts to the right. The mother was a primigravida; unremarkable pregnancy.

Consultations & Comments: Significance of Isolated Clinodactyly?

Sixteen-year-old boy referred to pediatric emergency department (ED) by his primary care physician with a history of headache, blurred vision, and mild proptosis of right eye. Vision: 20/200 OD (right eye) and 20/25 OS (left eye).

Eight-year-old girl with mass in midline of neck.Mass first noted about 6 months earlier. Patient is otherwise well; past health unremarkable. No symptoms ofhypothyroidism.

A 4-year-old girl presented with bilateral deviation of the fifth fingers. The deformity was noted in early childhood. There was no history of trauma or family history of a similar deformity. Physical examination was normal except for incurving of the fifth fingers.

Published: November 1st 2006 | Updated:

Published: February 1st 2006 | Updated:

Published: June 1st 2006 | Updated:

Published: January 1st 2007 | Updated:

Published: March 1st 2007 | Updated:

Published: February 1st 2006 | Updated: