Type 1 Diabetes
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

Psoriatic arthritis and spondyloarthritis occurred earlier in children and adolescents with IBD than in the matched references without IBD.

Integrated data from a continuous glucose monitoring device (CGM) and an insulin pump to automate insulin delivery allow AID systems to manage patient blood sugar levels more "effectively," according to Sequel.
A qualitative analysis shows adolescents and their parents more frequently report an unreadiness to transition from pediatric to adult type 1 diabetes care.
The device is intended for anyone aged 18 years and up who do not use insulin or those without diabetes who want to learn how diet can impact blood sugar levels.

A new study identified type 1 diabetes (T1D) as a risk factor associated with nearly all subtypes of CHD, whereas overweight was associated only with certain defect types.

Results demonstrated that caregiver burden scored a 2.14 on the caregiver burden scale, which is within the average burden level, though a higher burden of care is associated with a higher sense of loneliness. These results can help health care professionals develop a family-centered treatment plan.

A study in the European Journal of Medical Research revealed that higher maternal study satisfaction, older maternal age, and paternal participation were linked to better compliance in visits for children at risk of type 1 diabetes.

A new systematic review and meta-analysis found that the risk of type 2 diabetes decreased significantly at walking speeds of 4 km/h or above.
Mothers with mood disorders��—either bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder— or schizophrenia/ schizoaffective disorder are not associated with their offspring’s risk for type 1 diabetes, according to a recent study.

Reduced sleep efficiency and increased sleep irregularity in adolescents and young adults with type 1 diabetes are associated with higher HbA1c levels, insulin resistance, and endothelial dysfunction, highlighting the significance of addressing sleep-related factors in diabetes care for improved overall health.
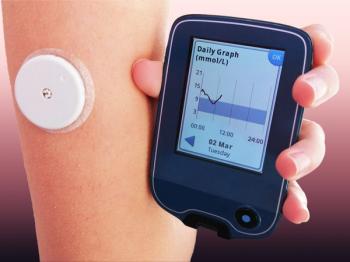
Continuous glucose monitors have been found to improve sleep for parents of young children with type 1 diabetes and may help alleviate the care burden associated with the condition, according to a study conducted in France.

According to the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), it is recommended that 45% to 65% of total daily calories come from carbohydrates, though very low-carbohydrate diets allow for 20 to 50 grams per day.

An analysis of the Diabetes Prevention Program in England found it was effective at improving key cardiovascular risk factors, including glycated hemoglobin and excess body weight.

Age-appropriate diabetes support for students is detailed, encompassing legal frameworks, healthcare plans, and the essential role of school health teams in effective school management.

In a systematic and meta-analysis review of cohort studies that featured nearly 1.7 million individuals, study authors concluded that there is an association between high body mass index (BMI) and an increased risk of incident type 1 diabetes (T1D).

There are a lot of challenges in the transition from youth to adulthood. For children and teens with chronic diseases like type 1 diabetes, these challenges—and the consequences they bring—only increase.

A new study says yes.

A significant improvement of stimulated C-peptide levels at week 78 for patients newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes (T1D) was observed for teplizumab-treated patients compared to placebo. Significant differences between groups for insulin dose, percentage of time in target glucose range, and change in glycated hemoglobin were not observed.

From 2006 to 2019, psychotropic medication use for those with type 1 diabetes (T1D) increased, leading investigators to call for risk-benefit studies, further evaluating effectiveness and improved diabetes care in this population.

The number of children who received a T1D diagnosis did not differ from children with and without SARS-CoV-2 infection.

In a recent study, the 2013 WHO criteria for diagnosing gestational diabetes mellitus had a low sensitivity when used in individuals in low-risk early pregnancy.

Surveys collected for a study published in the Canadian Journal of Diabetes revealed that desire for telehealth care amid pediatric diabetes families increased from the early onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, to more than 1 year later.
A recent article reviewed diagnosis and treatment methods of cystic fibrosis-related diabetes in pediatric patients.

The 2023 guideline for managing diabetes in children and adolescents highlights risk factors and treatment for type 1 and type 2 diabetes.

Numerous tools, technology platforms, and interventions have been developed to help teens with the difficult emotional and physical weight of managing the disease.














