Type 1 Diabetes
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
A recent article reviewed diagnosis and treatment methods of cystic fibrosis-related diabetes in pediatric patients.

The 2023 guideline for managing diabetes in children and adolescents highlights risk factors and treatment for type 1 and type 2 diabetes.

Numerous tools, technology platforms, and interventions have been developed to help teens with the difficult emotional and physical weight of managing the disease.

A new report examined the challenges of diabetes management during the school years from the perspective of the daily social and institutional challenges children face.

Expert endocrinologists provide final thoughts on addressing unmet needs and improving the management of T1D.

Schafer Boeder, MD, and Egils K. Bogdanovics, MD, share approaches to prevention, preservation, and replacement therapies for the treatment of T1D.

A new report reviewed how effective the use of continuous glucose monitors (CGM) was over the course of a year.

Previous studies have suggested that nighttime blood sugar fluctuations are a real problem—and a serious concern—for children with T1D and their parents.

Results of the randomized, multi-site study demonstrated the importance of early diabetes detection, as a single episode of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in young children with type 1 diabetes was associated with lower IQ scores soon after exposure.

Further studies are needed to determine if vaccination should be considered in children at risk for type 1 diabetes (T1D), as a COVID-19 diagnosis among children was associated with an increased incidence of T1D, according to a recent study.
A follow-up to an earlier study, the latest research leveraged EHR data from medical centers in North Carolina and concluded incident cases of type 1 diabetes increased nearly 50% and incident cases of type 2 diabetes more than doubled in 2021-2022 relative to prepandemic years.

Justin M. Gregory, MD, MSC, and Linda A. DiMeglio, MD, provide an overview of the pathophysiology of type 1 diabetes.

Schafer Boeder, MD, discusses the incidence of type 1 diabetes, highlighting risk factors such as age and family history.

To help teens with the difficult emotional and physical weight of managing this disease, numerous tools, technology platforms, and interventions have been developed. A research team recently published a review of one of these tools, a 40-year-old automated messaging system.

Despite the challenges of the pandemic, overall metabolic control didn’t significantly change during the lockdown.

Children 10 years and older with type 2 diabetes (T2D) can now be treated with empagliflozin and empagliflozin plus metformin hydrochloride to improve blood sugar control, per a recent approval by the FDA.

Intensive lifestyle change remains the primary treatment for youth-onset type 2 diabetes. According to a study in Jama Network Open, there is more work to be done as risk perception and awareness of diabetes alone were not associated with risk-reducing behaviors.

A recent study looked at how patients with type 1 diabetes used telehealth during the pandemic, and how it has influenced their preferred method of health care.

Results of the study, which was an analysis of accelerometry data the TEDDY study, indicate every 10-minute increase in daily moderate to vigorous physical activity was associated with an 8% reduction in risk of progressing to type 1 diabetes, but this association was not present among those who were single islet autoantibody-positive or single islet autoantibody-negative.
Part of the risk of developing kidney involvement begins when type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) sets in and establishes itself in the patient, with up to 65% of children experiencing acute kidney injury during T1DM onset, which can further predispose to the development of future chronic kidney disease.

The Beta Bionics iLet ACE Pump and the iLet Dosing Decision software, matched with a compatible FDA-cleared integrated continuous glucose monitor, use an algorithm to determine and command insulin delivery to users.

A hybrid closed-loop system can deliver glucose levels in the target range at a higher percentage of time among children aged 2 years to younger than 6 years compared to standard-care, according to a study in the New England Journal of Medicine.

In a recent study, offspring were more likely to develop type 1 diabetes if they were born to mothers diagnosed with depression or anxiety during pregnancy.
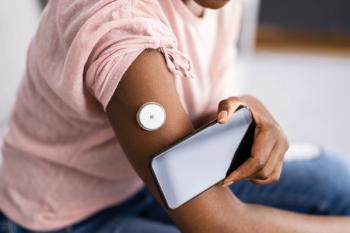
Hemoglobin A1c improved in youths with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes (T1D) when inclusive continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) was initiated, irrespective of ethnicity or insurance status. According to a study published in Jama Network Open, universal CGM could play a role in reducing disparities for minoritized racial and ethnic groups.

According to a recently published study, children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes (T1D) and psychiatric disorders have considerable increased odds for educational underachievement compared to those with T1D alone and healthy students.





