Vaccines
Latest News
Latest Videos
CME Content
More News
In a recent study, vaccination administered during pregnancy was effective against severe lower respiratory tract illness associated with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in infants.
A multi-country survey revealed 50% of meningitis vaccination appointments were delayed or canceled amid the COVID-19 pandemic, highlighting the need for “urgent action” to maintain routine vaccination levels among children, according to survey authors.
Pediatric experts review available COVID-19 vaccines for children and provide guidance on administration and advising parents/caregivers on when to vaccinate children.
Tina Tan, MD, and Sean O’Leary, MD, comment on the importance of vaccinating children against COVID-19, as well as how vaccine recommendations are changing.
Sean O’Leary, MD, reviews the different types of tests used to detect COVID-19 and their sensitivity and accuracy.

Tina Tan, MD, and Sean O’Leary, MD, discuss the evolving understanding regarding the severity and transmissibility of COVID-19 in the pediatric population.
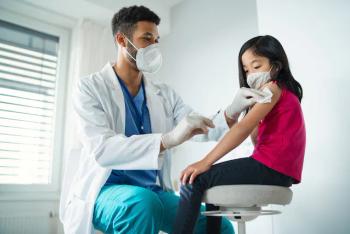
In a recent review, children with vaccination against human papillomavirus (HPV) initialized at a younger age were more likely to receive their full vaccination series.
If approved by the FDA, this 5-in-1 investigational candidate could provide the broadest meningococcal serogroup coverage.

At the 44th National Association of Pediatric Nurse Practitioners Conference, the CDC provided an updated immunization schedule, detailing new changes.

A new booster shot of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine is now available for young children to help protect this population against serious COVID-19 effects.
In a recent study, children aged 5 to 11 years were less likely to be hospitalized with the Omicron strand if they received vaccination against COVID-19.
In a recent report from the CDC, monovalent vaccines from Moderna and Pfizer have shown vaccine effectiveness in children aged 3 to 5 years in at least the first 4 months after vaccination.

A booster dose of mRNA COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy increases protection of infants from infection and related hospitalization.

The 2023 changes include vaccines for influenza, pneumococcal disease, measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) and COVID-19.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved another Tdap vaccine option for use during pregnancy to prevent pertussis, otherwise known as whooping cough.

The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has provided an updated safety profile on the bivalent COVID-19 booster vaccine in children aged 5 to 11 years, showing similar adverse events to the monovalent vaccine.

Patients with a history of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) completed a questionnaire about adverse reactions following COVID-19 vaccination, and no serious adverse events were recorded.
In a recent report, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that the JYNNEOS vaccine for preventing monkeypox has not caused severe adverse events in patients aged under 18 years.
A recent analysis showed that vaccine-associated myopericarditis was rare in adolescents and young adults, and that outcomes were favorable.

The US Food and Drug Administration has updated the emergency use authorization for bivalent COVID-19 vaccines to be available for children aged 6 months and older.

Bradley Warady, MD, pediatric nephrologist and researcher at Children’s Mercy Kansas City, discusses the causes of vaccine hesitancy and the effects of vaccine hesitancy on public health.
A recent poll showed that some parents do not discuss vaccines with their child’s regular doctor, with many choosing to not have their child receive any vaccines.

A real-world study determined the efficacy of mRNA vaccines for protection against COVID-19 in adolescents.
Confidence in vaccines is lower post-pandemic across all demographic groups.

Despite vaccine effectiveness against human papillomavirus, many individuals do not receive vaccination prior to sexual debut, as recommended by the ACIP.