
The first meeting of the Committee on Assessment of Studies of Health Outcomes Related to the Recommended Childhood Immunization Schedule was held in February in Washington, DC, at the Pew Charitable Trust.

The first meeting of the Committee on Assessment of Studies of Health Outcomes Related to the Recommended Childhood Immunization Schedule was held in February in Washington, DC, at the Pew Charitable Trust.

A breath test that detects Helicobacter pylori infection has been approved by the US FDA for use in children aged 3 to 17 years.

Physicians meeting a child and family for the first time must inspire confidence, display empathy, and develop trust while providing knowledgeable, evidence-based care, meeting diagnostic challenges, and, often, coordinating consultation from multiple services.

Significant economic and educational issues surround teenage pregnancy, the goal being to avoid as many unplanned pregnancies as possible.

The US Food and Drug Administration has notified medical care organizations and health care professionals about a class 1 safety recall on certain models of perinatal pediatric hospital bassinets because of defects that may put infants at risk.

The mother of a 17-day-old boy with Down syndrome calls the physician over the weekend worried about increasing swelling, redness, warmth, and yellowish-brown drainage from the umbilicus over the last 8 hours.

Functional abdominal pain in children can be a tough nut to crack. Organic causes should always be excluded, but after that, treatment modalities are many and varied.

It's time for Dr Michael Burke's annual list of the 10 best articles he's reviewed for Journal Club over the past 12 months.

Investigators sought to determine how often emergency department providers, pediatric residents, and nurses document screening for secondhand smoke exposure, an important cause of mortality and morbidity among children.

A study conducted in a hospital-based clinic serving mostly low-income families shows that mothers and other infant caregivers generally accept free Tdap vaccine when it is offered during an infant's 2-week well-child visit.

The case reads: 6-week-old female with twitching episodes. It helps to educate yourself regarding the Moro reflex.

A working group has proposed a set of criteria to define a newly named entity - pediatric acute-onset neuropsychiatric syndrome - the most important of which is an abrupt, dramatic onset of obsessive-compulsive symptoms.
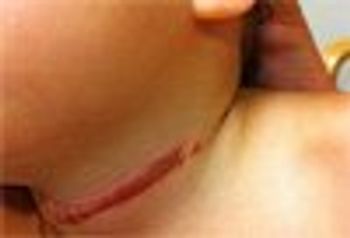
A mother presented to the ED with her 3-year-old child asking about an upper respiratory infection and an incidental wound around the child’s neck.

A mother presented to the ED with her 3-year-old child asking about an URI and an incidental wound around the child’s neck. She said that the child got tangled in a dog leash.
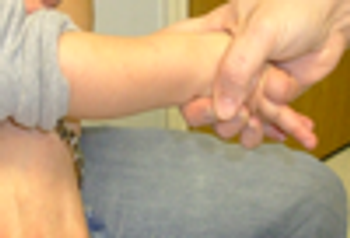
This 4-year-old boy returned home after a day at a small private daycare with a bite mark on his forearm.

Parainfluenza virus is the most common cause of croup, while bronchiolitis is usually caused by respiratory syncytial virus. Read about diagnosis and treatment of these conditions.

A survey of pediatricians from Connecticut reveals that more parents are refusing vaccines for their children, and pediatricians are increasingly dismissing families from their practices for vaccine refusal. How would you address the concerns of such families in your practice? There are tools available to help.

Over the years, children’s sleep has consistently fallen short of recommendations, although it has never been established exactly how many hours children of different ages should be sleeping. One new study shows that actual sleep time is decreasing, whereas another suggests that current guidelines may not accurately reflect the amount of sleep children need for optimal school performance. Find out why children never seem to get enough sleep, despite changing guidelines.

One in 10 children younger than 18 years lives with a parent who has experienced an alcohol-use disorder in the past year, setting them up for subsequent biological, psychological, and environmental problems. There are a number of resources available to practitioners to help identify these children and to help them and their families.

An ongoing study that could lead to an imaging biomarker for autism as early as 6 months, before the onset of observable behavioral symptoms, may also eventually provide practitioners an avenue for earlier intervention in autism spectrum disorders

Use of electronic health record (EHR) computer-assisted decision tools can increase identification, diagnosis, and counseling for overweight and obese children and adolescents, a study of a large pediatric population suggests. Find out how these tools can help overcome barriers to weight management for your patients.

The California Department of Public Health and the California Family Health Council have launched a new project that is designed to reduce the rate of transmission of sexually transmitted diseases among teens by making free condoms available year round. Could such an initiative work in your state? Learn about the details of this innovative program.

Preterm infants born with extremely low birth weights have an increased risk of death during the first years of life. Find out why it is important to identify and try to correct modifiable factors that account for increased mortality in very premature infants after hospital discharge.

Clinicians can avoid exposing asymptomatic infants to ionizing radiation by substituting ultrasound for plain radiography as a reliable screening modality for developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH). New research allays clinicians’ growing concerns about using radiation in very young children to detect this common congenital birth defect.

A multicomponent meningococcal B (4CMenB) vaccine induces an immune response in healthy infants and can be given safely with other routine vaccines, according to a European multisite, randomized study. Read why study results suggest that 4CMenB can be incorporated into various immunization schedules.

Children younger than 1 year and children on Medicaid are the most likely to suffer serious injuries because of physical abuse, according to an analysis of data from a US database. The study was the first to provide estimates on the number of US children hospitalized as a result of serious injuries from physical abuse. Learn what data identified poverty as a major risk factor for abusive injuries.

Spanking used as discipline for children is increasingly linked to long-term negative behaviors in adults and even physical alterations of cognitive areas of the brain, say researchers from Canada. Their analysis of 20 years of published research suggests that physicians should reexamine the issue of physical punishment from a medical perspective and advise parents to seek alternative methods to modify their children’s behavior.

Children with burns covering 60% or more of their total body surface area (TBSA) are at increased risk for complications and death and should be transferred immediately to specialized burn units, according to a new study. What critical factors determine prognosis in children with severe burns?

Child psychiatrists and neuroscientists at Washington University found that children who are nurtured and shown love and affection from the earliest days of their lives have brains with a larger hippocampus, the key part of the brain involved with memory, stress response, and learning. Find out more about how this study and its provocative findings add to previous studies of nurturing.

Assessing underlying risk factors for childhood stroke is important to survival and quality of life. New findings suggest that recent minor acute infections of the ear, upper respiratory tract, and urinary tract can pose a high risk of ischemic stroke in children. These are common pediatric occurrences, so how can you identify patients at risk?