
Tablets, smartphones, and apps are a part of daily life for many children. Unfortunately, those same apps could be giving third parties identifying information, according to an investigation.

Tablets, smartphones, and apps are a part of daily life for many children. Unfortunately, those same apps could be giving third parties identifying information, according to an investigation.

The influenza season is going to be here soon, which could make things difficult for a system already taxed by COVID-19. A new report illuminates the similarities and differences between COVID-19 and seasonal influenza.

Eating disorders can be devastating and could lead to damage or even death. Can digital cognitive behavior therapy help?

Children zoom all over the place in their play. A new meta-analysis looks at how the cardiorespiratory fitness from that running could impact later life health.

Cancer in adolescents and young adults isn’t common. What symptoms spur a visit that starts the path to diagnosis? A report provides some information.

Stricter minimum age laws have helped improve outcomes for tobacco and other things. Do such laws have a positive impact on firearm homicide rates in young adults?

Endocrine-disrupting chemicals are nearly ubiquitous in day-to-day life. Could they be linked to attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder-like (ADHD) behavior?

Oral immunotherapy is promising in the treatment of food allergies, but not every patient—and not every physician—can take it on.

The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Medtronic’s hybrid closed loop diabetes management device for use in children aged 2 to 6 years.
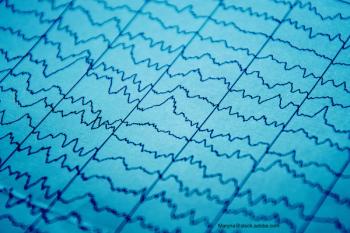
Diagnosing neonatal seizures can be complicated and difficult. Could an algorithm help? An investigation examines.

Food insecurity has been tied to obesity, but little is known about whether this link extends to infants. A new study looks at whether this connection holds.
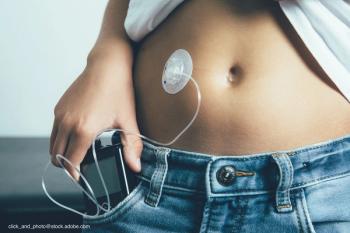
Type 1 diabetes treatment has improved dramatically over the years. A new study examines the efficacy of a closed loop system.

The Healthy Choices intervention has been shown to be effective with managing HIV, but is it better when provided at home or in the clinic? A new report sheds some light.

A recent report reveals some of the problems with electronic health records (EHRs), and what pediatricians can do to help.

Reporting symptom burden and pain can be fairly subjective and they can become even more subjective when reported by proxy. A report examines how caregiver reports vary from a child’s report during treatment of pediatric cancer.

Active shooter drills have become a fact of life for America’s school children. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) has issued a policy statement on them.

Good communication is a necessity to ensure optimal care for children. A new report looks at what parents look for when communicating with clinicians during pediatric cancer experiences.

Research is key to improving children’s care. How much does the informed consent form factor into a parent allowing their child to participant in research studies?

Water fluoridation has been shown to reduce dental caries, but can it reduce the dental surgery in Medicaid patients? A new study takes a look.
Although improvements are modest, community interventions may help improve health care usage.
Adolescence can set the course for a person’s health for life. A new study looks at how physical activity can impact hip strength and potentially reduce the risk of osteoporosis.

Burnout is often seen as something that happens to physicians who have been practicing for years. A new study looks at how burnout impacts trainee physicians.

The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a supplemental Biologics License Application XEOMIN® (incobotulinumtoxinA).

Introducing foods is a milestone in every infant’s life, but are practitioners giving the best advice to uncover any food allergies? A survey study provides some answers.

How parents feel about their child returning to school during a pandemic hasn’t been at the forefront of the school return debate. A report provides some much needed information about how they feel.

Mental health can have a major impact on a person’s life. A report looks at how mental health problems in early life can have a toll on some health behaviors.

Psychiatric hospitalization can be a necessary step to keep children safe, along with follow-up care after discharge. A study looks at whether timely follow-up can help lower the risk of suicide.
Opioids are linked to substance-related morbidity and a new study looks at what morbidity looks like in adolescents and young adults.

The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Evrysdi (risdiplam) to treat spinal muscular atrophy. It is the third drug approved to treat the condition.

Screenings are an important way to ensure that children get referred to necessary care, but gaps still remain. A new study reports on whether a quality program improved screening rates.