Infections and how they are treated early in life may impact how mental health disorders develop early on, according to a new report, highlighting the need for a better understanding of the mind/body connection.

Infections and how they are treated early in life may impact how mental health disorders develop early on, according to a new report, highlighting the need for a better understanding of the mind/body connection.
Lymph node enlargement is common in children. Focused assessment and quick diagnosis of cause are key to ensure proper treatment.

Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and Influenza are responsible for significant morbidity and mortality in children. Pediatricians must step up vigilance to ensure early diagnosis and treatment.
A new study has identified a higher risk of severe respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection-with higher hospitalization and mortality rates-in children with Down syndrome.

Adhering to a 1-hour plan for blood culture collection, and administering fluids and antibiotics, helped improve outcomes across New York hospitals in pediatric sepsis cases.
Despite the high prevalence of congenital cytomegalovirus, many pediatricians and even obstetricians lack knowledge and awareness of the adverse sequelae of this disease on children.
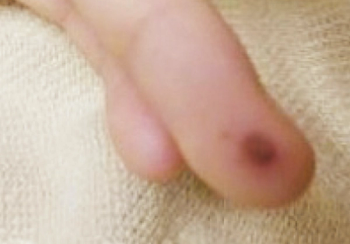
A 15-year-old Caucasian male with a past medical history of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder presents to the hospital emergency department with a 1-week history of fever, headache, arthralgias, vomiting, and rash.

A change in the H1N1 component may have solved efficacy problems from prior formulations of the intranasal vaccine.

There are two articles in the March 2018 issue of Contemporary Pediatrics that merit your attention: Dr. Bass’ article on “Is it the flu?” and Ms. Zimlich’s article on “Major vaccines addressed in updated ACIP guidelines.”

There are some notable revisions in 2018 to recommendations concerning hepatitis B vaccination for newborns and a third dose of mumps-containing vaccines, among others.

When and how to use rapid testing for influenza

Consider these helpful hints when diagnosing anemia or infections in your patients.

For Contemporary Pediatrics, Dr Bobby Lazzara discusses a practice update published in the Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology regarding egg allergies and administration of the influenza vaccine.

Pediatricians need to stay committed to following those infants with possible exposure to Zika to understand the effects of Zika infection and ensure appropriate care and services.

A new study reviewing whether drinking water before vaccination could help dispel feelings of postvaccination dizziness found instead that anxiety before the shot may be a bigger factor.

The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) is reporting that despite the lack of an intranasal option, there has been no substantial decline in flu vaccination among children.

A novel assay for distinguishing bacterial from viral infections significantly outperformed routine laboratory parameters and biomarkers in a study using serum remnants from children suspected to have acute infection.

For Contemporary Pediatrics, Dr Bobby Lazzara discusses a recent statement published in Pediatrics that discussed key ways to prevent and control infection in ambulatory settings.

The American Academy of Pediatrics stresses the importance of vaccinating all children aged older than 6 months early in the season for the best flu protection.

A study of Mycoplasma pneumoniae disease during an epidemic in Norway found that preschool children infected with this bacterium had a significantly higher risk of severe disease, particularly severe pneumonia, than school-aged children.

From ear infections to croup to strep, I have found that the simplest diagnosis is often the best diagnosis.

Visually oriented social media platforms created by their peers can have a significant negative impact on adolescents’ body image.

For the first time in a decade, there are antibiotics newly approved for use in children with skin and skin structure infections that do not respond to conventional treatment.

Every pediatrician has experience with influenza and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), but there are still many cases in which these illnesses are misdiagnosed or mismanaged.

Breastfeeding is already known to offer a number of health and developmental benefits. Now, an Australian study is adding ear infection prevention to that list.