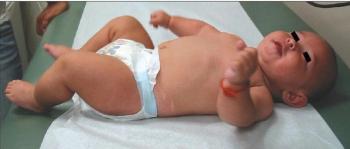
HISTORYBaby boy born at full term via forceps-assisted vaginal delivery to a 17-year-old primigravida was noted to have left arm and chest anomalies. Apgar scores 9 at 1 minute and 9 at 5 minutes. No pregnancy complications except for low amniotic fluid index. Second trimester ultrasonogram showed no malformations. At birth, infant was vigorous. He tolerated feeding well and passed urine and stool appropriately. Results of a hearing screen and newborn metabolic screen were normal. No family history of genetic disorders.PHYSICAL EXAMINATIONClinically, infant was asymptomatic. Vital signs normal. Weight, height, and head circumference (3.040 kg, 50.8 cm, and 33 cm, respectively) appropriate for gestational age. He had a flat left upper chest, an abnormal and caudally displaced left nipple, hypoplasia of the muscles of the upper left shoulder girdle and arm, significant shortening and bowing of the left forearm, and left hand cutaneous syndactyly. The left thumb resembled a finger and was not opposable. Heart sounds heard best to the right of midline, corresponding to dextroposition of the heart. No heart murmurs. Remaining physical findings unremarkable.WHAT’S YOUR DIAGNOSIS?(Answer and discussion on next page)ANSWER: POLAND SYNDROMEPoland syndrome, also known as Poland sequence, is a rare congenital anomaly characterized by unilateral chest wall hypoplasia and ipsilateral anomalies of the upper extremity. The condition, first described by Dr Alfred Poland in 1841, was officially named in 1962 by Dr Patrick Clarkson, who reported on 3affected children. The incidence of Poland syndrome is 1 per 20,000 to 30,000; however, it is believed to be underreported. The syndrome is 3 times more likely in males than in females; the right side is favored over the left.1ETIOLOGYDiminished blood supply to the affected side secondary to developmental defects of the subclavian artery is the suspected cause of Poland syndrome. Maternal drug abuse during pregnancy has been reported.2,3 Most cases of Poland syndrome arise sporadically. Familial cases have been described, which suggests some degree of genetic transmission. However, a case of Poland syndrome in one identical twin has been reported.4CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONSThe minimum criterion needed for diagnosis is unilateral absence or hypoplasia of the sternal portion of the pectoralis major muscle. Other classic features on the ipsilateral side include:
•Hypoplasia or aplasia of the breast and nipple.
•Deficiency of subcutaneous fat and axillary hair.
•Abnormalities of the rib cage.
•Upper extremity anomalies, such as short arm and fingers as well as syndactyly.2It is not rare for infants with Poland syndrome to have all the classic features. Intelligence is not impaired in children with this syndrome.